Chang Tsi & Partners | View firm profile
- Overall Review of China Free Trade Zones
Since 2013, Free Trade Zones (“FTZ”) in China have emerged increasingly, totaling 22 today as shown below,and formed unique characteristics of their own in China. Contributions of FTZ are tremendous, for example in 2023, total import and export volume reached 7.67 trillion yuan, increasing of 2.7%, and accounting for 18.4% of the total value of imports and exports.
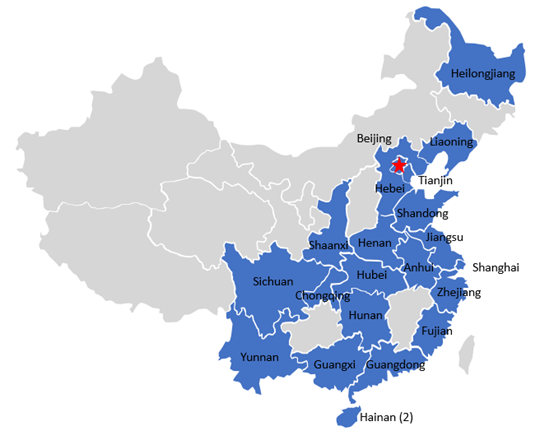
There are several key features for China FTZs:
1.1) Openness: lower barriers, simplify administrative approval procedure, broaden market entry, optimize business environment
1.2)Institution innovation: test new policies and administrative measures, explore new modes
1.3) Differentiated positioning: Different free trade zones have different development positioning and pilot tasks based on the economic characteristics and strategic needs of their respective regions. Some free trade zones focus on developing specific industries, while others focus on promoting regional economic integration and international cooperation.
1.4) High quality development: By supporting the development of emerging industries such as high-tech industries and modern service industries, promote the optimization and upgrading of industrial structure, and improve the quality and efficiency of economic development.
1.5) International cooperation: Free trade zones actively participate in international economic cooperation, strengthen international trade and investment connections, and promote global economic integration by establishing free trade zones, economic cooperation zones, and other forms with other countries.
1.6) Environment of laws: protect rights and interests of enterprises
- Features and Measures of IP Protection, IP Commercial and General Commercial Policies
2.1 Patent Side
1) Policy support: FTZ usually enjoys the tilt and support of national policies, including simplification and acceleration of patent examination and authorization processes, fiscal incentives, tax incentives, etc.
Advantages in the patent examination process: providing priority examination channels. For example:
Provide priority patent examination channels for key development industries and strategic emerging industries; If the patent administrative department fails to make an examination decision on an invention patent application after 18 months, the patent application information shall be disclosed. For those who do not meet the relevant requirements after preliminary examination or require further examination, the reasons should be explained. The patent administrative department may announce the application results in advance based on the application; Promote rapid pre examination, rapid property rights confirmation, and rapid rights protection, and shorten the average authorization period for invention patent applications of filing units from 3 years to 3 months.
Financial incentives: Free trade zones usually have fiscal, financing, and tax incentives for patents. For example: Financial service models such as pledge financing, financing leasing, and trust; Carry out overseas intellectual property infringement liability insurance, patent execution insurance, patent infringement loss insurance and other insurance businesses; tax deduction for IP incomes.
Local government assistance measures: The government in the location of the free trade zone usually provides various assistance measures for patent application, patent protection, patent system, etc.
2) Aligning with international rules: utilize internationally recognized patent practice rules and expand their global technological influence through international cooperation. Additionally, local judicial institutions in free trade zones also provide convenience for international legal procedures related to patent protection.
3) Strengthening intellectual property protection: specialized institutions (such as technical investigators, intellectual property courts, arbitration institutions, and comprehensive administrative law enforcement agencies in cities, counties, and autonomous counties with patent enforcement conditions), providing more efficient and professional ways to resolve intellectual property disputes.
2.2 Trademark Side
1) Docking with international high standard economic and trade rules: In terms of intellectual property protection, the free trade pilot zone pays more attention to docking with international high standard economic and trade rules.
2) Strengthen the connection between border law enforcement and domestic law enforcement, and enhance judicial protection: In free trade pilot zones, specialized intellectual property trial tribunals or courts are usually established to improve the quality and efficiency of intellectual property litigation services. For example:
-
- The Guangdong Pilot Free Trade Zone Guangzhou Nansha New Area has established an intellectual property trial court, providing bilingual and simplified litigation guidelines in both Chinese and English, and promoting the self-service terminal of “E Court”.
- The establishment of the Shanghai Intellectual Property Court is aimed at concentrating the trial of intellectual property cases related to the free trade zone, improving the professionalism and efficiency of the trial. At the same time, the Shanghai Intellectual Property Court has established a special collegial panel for intellectual property cases in the Free Trade Zone, which is specifically responsible for hearing intellectual property cases related to the Free Trade Zone, ensuring the professionalism and efficiency of case trials.
- Actively promoting the “three in one” trial mechanism for intellectual property civil, administrative, and criminal cases
- Cross class special protection for unregistered well-known trademarks: If an unregistered trademark used for different or dissimilar goods or services is a copy, imitation, or translation of another person’s unregistered well-known trademark in China, misleading the public and causing potential harm to the interests of the holder of the well-known trademark, its use is prohibited within the Hainan Free Trade Port.
- Encourage mediation for disputes
- Promote ad hoc arbitration
- Administrative temporary injunction
- Blacklist and double punishment for repeated infringement: Establish a blacklist system for seriously dishonest entities in the field of intellectual property
3) Law Enforcement Cooperation and Mutual Aid: The Free Trade Pilot Zone will also establish an Intellectual Property Law Enforcement Cooperation and Mutual Aid Center. For example, the Xiamen Free Trade Zone in Fujian Province has established an Intellectual Property Law Enforcement Cooperation and Mutual Aid Center, dedicated to bridging the entire chain of regulation, law enforcement, and justice. The center will focus on providing assistance for enterprise intellectual property rights protection, law enforcement cooperation between relevant departments within and outside the zone, and the connection between intellectual property administrative law enforcement and criminal justice. It will fully leverage the geographical advantages of the Xiamen Free Trade Zone and carry out intellectual property protection work across regions and fields. Promote cooperation and mutual assistance between intellectual property management departments, use the “Internet plus” information platform to improve early warning and prevention functions, achieve diversified and collaborative intellectual property protection, systematize and institutionalize intellectual property law enforcement in the Free Trade Zone, and improve law enforcement and comprehensive supervision capabilities in the field of intellectual property
4) Customs protection: Free trade pilot zones also have special regulations and measures in terms of customs protection. For example, according to Article 51 of the Agreement on Trade Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights, member states take border protection measures against goods suspected of importing pirated or counterfeit trademarks. China’s free trade zones implement basic intellectual property customs protection that meets the minimum standards of international treaties at the “first line” checkpoints, while comprehensive intellectual property customs protection is implemented at the “second line” checkpoints
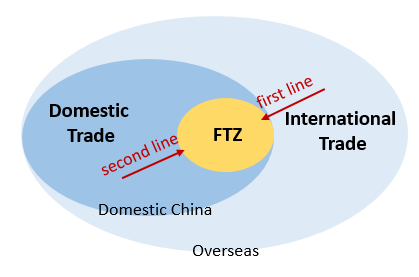
5) Overseas Rights Protection: The Free Trade Pilot Zone also pays attention to the issue of overseas rights protection of intellectual property, establishes a multi departmental coordination and linkage mechanism for overseas rights protection assistance of intellectual property, establishes an overseas warning service platform for intellectual property, and provides enterprises with intellectual property risk warnings, emergency measures, and proactive prevention services.
2.3 IP Commercial and General Commercial Side
1)IP Commercialization:
IP Finance: FTZs are incentivized to pioneer innovations in IP pledge financing models, formulating specialized financing products that are predicated on the assessment of a corporation’s IP assets and its overall capacity for innovation. Through the development of dedicated platform carriers, these initiatives aim to facilitate the online dissemination, transaction processing, and intermediary services for the registration of IP pledge financing, ultimately streamlining the financing process and augmenting efficiency.
IP licensing and transfer: FTZs also encourage the licensing and transfer of intellectual property rights to boost the vitality of high-tech industries. For instance, Several Policies to Support the High-Quality Development of Intellectual Property Rights in the China (Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade Zone Lin-gang Special Area offer financial incentives to universities, research institutes, and companies when they are engaging in patent licensing and transfers to external parties.
2) Data compliance:
Data transfer negative list: FTZs are now set to introduce policies designed to streamline and enhance the efficiency of cross-border data transfers. Article 6 of the Regulations on Promoting and Regulating Data Cross-Border Flow specifies that FTZs are obligated to compile a negative list of data, which falls within the scope of the national data classification and grading protection framework. This can ensure smoother and more expedient cross-border data flows.
International data hub: The White Paper on the 10th Anniversary of China (Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade Zones proposes articulates a commitment to establishing a secure and orderly protocol for cross-border data flow. This includes a measured approach to the development and expansion of the international data hub in Lin-gang Special Area. The Management Measures for the Classification and Grading of Cross-border Data transfer in the Lin-gang Special Area (Trial) are implemented accordingly.
3) Import and Export: FTZs are known for their liberalized policies regarding imports and exports. For example, the Several Measures for Conducting the Pilot Program of Aligning with International High Standards and Promoting Institutional Opening up in Eligible Pilot Free Trade Zones and the Hainan Free Trade Port aim to bolster the pilot regions by facilitating import for remanufactured products within key industries. These measures also include provisions for tariff exemptions on specific categories of imported and exported goods, and they explicitly forbid the refusal of preferential tariff rates for goods due to non-material concerns, thereby ensuring a more streamlined and equitable trade environment.
4) Tax: FTZs generally provide companies with various tax benefits, In a significant move, the Ministry of Finance and China’s State Taxation Administration officially issued the Notice by the Ministry of Finance and the State Taxation Administration of Launching the Pilot Program of Preferential Stamp Tax Policies for Offshore Trade in the China (Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade Zone and the Lin-gang Special Area in February of this year. The Notice specifies that from April 1, 2024, to March 31, 2025, sales contracts executed for offshore transfer trading activities by enterprises registered in the China (Shanghai) Free Trade Pilot Zone and the Lin-gang Special Area will be exempt from stamp duty.
- Strategies for IP Right Holders
3.1Patent Perspective
1) Optimize patent portfolio: Proprietors may, based on their market strategies, utilize the various policies which are favor for patent applications offered by the free trade zones, and consider the specific needs both inside and outside the free trade zone, formulate an efficient and rational comprehensive patent portfolio strategy.
2) Optimize patent quality: Proprietors may be focusing on the patent quality rather than the quantity of patents, ensuring that each patent possesses strong market competitiveness and high legal validity.
3) Facilitate patent enforcement: Proprietors may utilize mechanisms such as patent navigation and rights protection guidance provided by the free trade zones to promptly detect potential infringement activities and take effective measures to enforce patent rights.
4) Balance the protection of trade secrets and patents: Proprietors may make reasonable use of the various resources in the free trade zones to differentiate and select between the protection of trade secrets and patent applications, in order to maximize the overall value of intellectual property.
3.2 Trademark perspective
1) Customs recordation: As mentioned above, although the formalities for the entry of goods are simplified in a FTZ, customs inspections are still performed for the import and export of goods. The recordation of IP with customs is therefore still an effective way to stop the flow of infringing goods passing through a FTZ. Given the focus on speed of inspections, the creation of FTZs has made the adoption of customs recordation and customs training imperative for IP owners to employ the reduced benefits of customs inspections. Clients shall take advantage of these customs procedures to record its IP, set up training sessions, and prepare training materials on its key intellectual property to make it easier for Customs to help IP owners at the border.
2) Administrative complaints: Filing an administrative complaint with the AMR or Intellectual Property Office (dual track for patent complaint) in FTZs is a cost-effective tool: speed, low-cost, and effectiveness; By way of administrative mediation, the right holders’ demands can also be met.
3) Judicial remedies: Civil and criminal remedies are increasingly in demand in China’s FTZs, as is the court’s willingness to grant preliminary injunctions, in the appropriate cases; Claims for damages have been steadily rising as well.
3.3 IP Commercial and General Commercial Perspective
1) IP commercialization and technological innovation
FTZs continue to benefit from distinctly advantageous policies that bolster IP commercialization. Moreover, these zones demonstrate a robust commitment to fostering technological innovation. While capitalizing on the current policy framework, it is also encouraged to remain vigilant for annual updates to preferential policies, including those related to high-tech subsidy applications.
2) Innovation of export and import system
Last year, some IP holders adeptly navigated the new policy of the FTZ to facilitate China’s first import of remanufactured engine. By continuing to delve into and harness the advantageous import and export policies specific to the FTZ, right holders are poised to catalyze substantial development and amplify its profitability.
3) Data transfer facilitation
Present regulations and policies are providing a conducive environment for the cross-border data flow and the expansion of digital trade within FTZs. This year is particularly notable with the ongoing development of the Shanghai International Data Hub, which is anticipated to enhance the capabilities of enterprises. Utilizing the advanced services like the Data Flow Service Center in the Lin-gang Special Area, companies are expected to experience streamlined data transfer, improved compliance processes, and more efficient digital trade facilitation.
4) Tailored tax policies
The PRC government continues to introduces progressively advantageous tax policies tailored for FTZs. Companies that maintain a strategic emphasis on and thoroughly leverage these incentives are poised to realize substantial enhancements in both economic performance and competitive advantage.
In conclusion, it appears the laws and mechanisms for the prosecution and the enforcement of IP rights in FTZs are actively being utilized by IP owners. We recommend that clients take advantage of existing patent prosecution policy and rules, IPR customs procedures, IPR administrative procedures with the AIC or Intellectual Property Office, as well as court rules, so that they can obtain rights and find and stop infringement as early as possible.