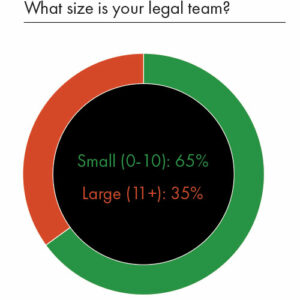
Of the 140 people who participated in our research, 65% of those were from small legal teams, with the remaining 35% coming from larger teams. The attitudes, ability and budgets of these two different groups had a number of notable differences – and not always in the way one might typically expect.
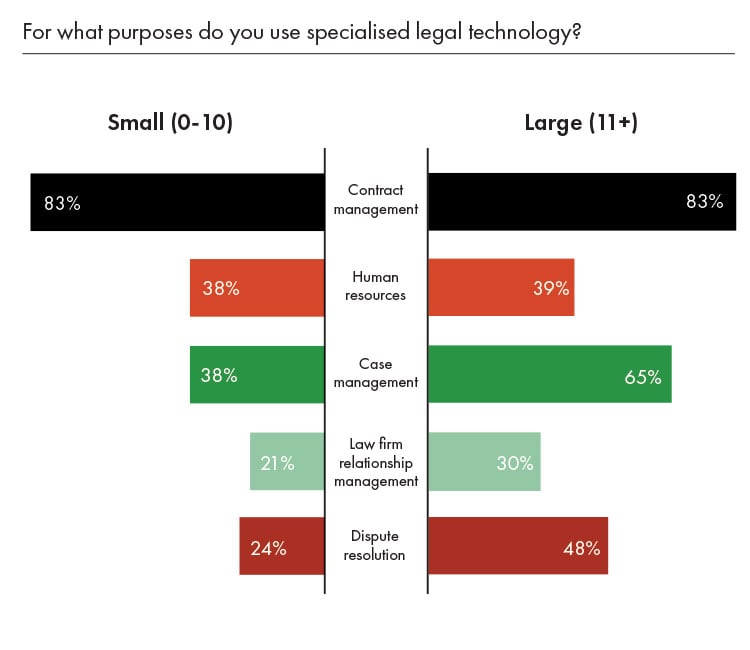
While our research showed that the overwhelming majority of all legal teams in Latin America used specialised legal technology in some form within their department at 96%, the few that didn’t all came from respondents from small legal teams. How that technology was used was relatively similar between the two different groups in most areas – use for factors like contract management, human resources and law firm relationship management was nearly identical. Where large teams did differ was with case management and dispute resolution, where large legal teams were nearly twice as likely to use specialised case management and dispute resolution technology.
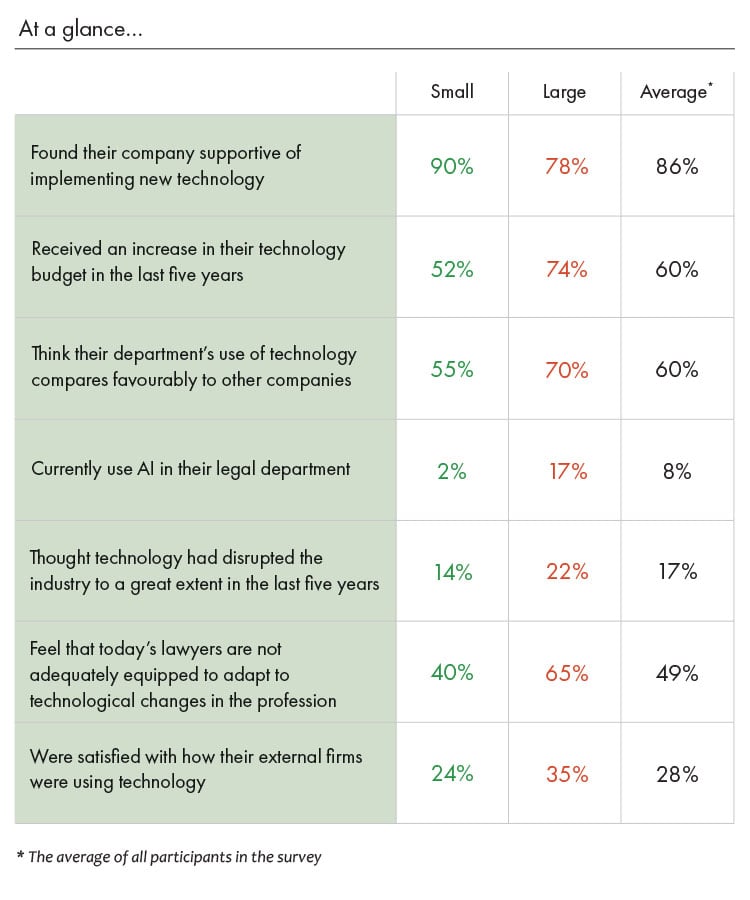
The vast majority of our respondents held a positive outlook on the extent that they believed technology could enhance outcomes for in-house departments, with 66% of all respondents believing it can enhance to a great extent and 31% to a moderate extent. Those from larger teams, however, retained an even more upbeat stance than their smaller counterparts: 85% of those from larger legal teams believed that technology could enhance outcomes to a great extent, compared to 56% of those from smaller teams.
Larger teams were also more likely to have a positive outlook on how their department fared compared to their peers. While the majority of small legal teams retained a positive outlook, at 55%, that number was dwarfed by large legal teams, where 70% said they thought that their department’s use of technology compared favourably with other companies.
Interestingly, while small legal teams were much less likely to have received an increase in their technology budget over the last five years compared with their larger counterparts, that didn’t necessarily translate to feeling unsupported by their company when implementing new technology. While only 52% of small legal teams had received a boost to their budget, 90% of those we surveyed from small legal teams felt that their company was supportive. Compare that to larger legal teams, where 74% had received an increase in their tech budget, but only 78% felt that their company was supportive.
Based on the interviews that complemented the quantitative component of the research, the reasons for in-house legal teams feeling supported by their companies were more nuanced than simply being given the green light to purchase new services. Getting buy-in from the wider company was important to a number of those who we spoke with, with a range of factors noted, including assistance with integrating legal systems across the wider business.
While artificial intelligence remained a rarity in legal departments across Latin America, it was currently being used almost exclusively in large legal teams. Those we spoke to who utilised AI tended to have legal teams that were at the top end of large – with upwards of 50 members on their team – and were primarily utilising it in order to either reduce the more menial tasks their businesses required from legal, or to assist in departments that had large amounts of litigation and disputes work.
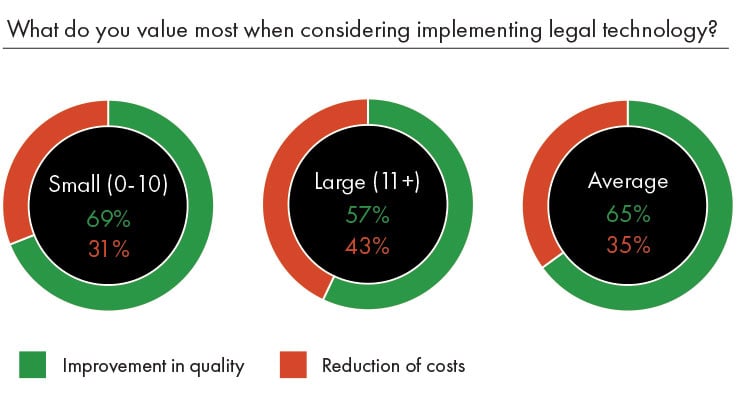
That attitude broadly aligned with the reason behind technology implementation. Between the two groups, what was most important when considering legal tech was one area where there was a difference. While smaller teams were mostly concerned with using technology to improve the quality of their work, at 69%, those from larger legal teams were less likely to value improvement of quality, at 57%, and put a higher priority on using technology to reduce costs.