LuxLeaks, Cambridge Analytica and the Panama Papers are just a few examples of recent scandals propelled to the public’s attention by whistleblowers. Workers are increasingly speaking up against corruption, fraud, sexual harassment and harm and, in the process, preventing scandals from progressing and even saving lives. Yet some have encountered retaliation or have simply been ignored.
But this is set to change.
Piecemeal action by governments over recent years had already started to strengthen whistleblower (also known as ‘protected disclosure’) laws. However, the European Union’s agreement in April 2019 to implement comprehensive new whistleblowing legislation across its 28 member states marks a significant step change – one which will have practical workplace consequences beyond Europe.
In particular, those multinationals applying a one-size-fits-all global whistleblowing policy will need to decide whether to apply the EU’s higher standards beyond Europe. Considerations will include issues such as whether to make reporting channels available to contractors and suppliers, broadly defining protected disclosures, as well as requiring investigation and the provision of feedback to disclosers within three months.
In this age of the whistleblower, employers failing to provide easy access to confidential reporting mechanisms or handling disclosures and disclosers inappropriately risk problems escalating, reputational damage and, increasingly, significant sanctions for breaching whistleblowing regulation.
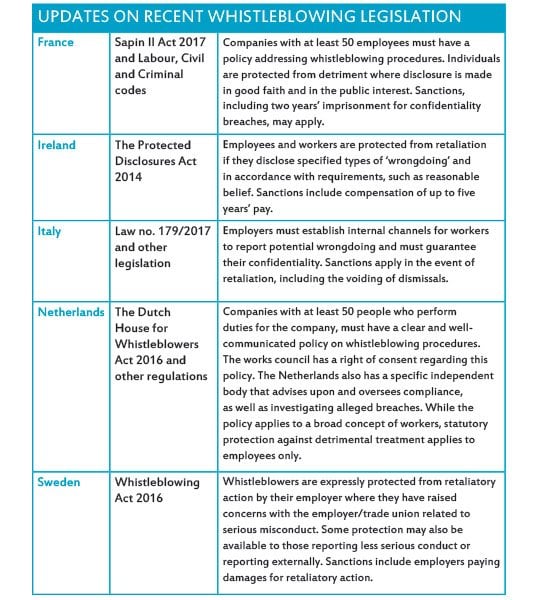
Recent legislative changes to whistleblowing protections
In 2018, the EU listed ten member states with comprehensive whistleblower legislation in place (Ireland, France, Hungary, Italy, Lithuania, Malta, the Netherlands, Sweden, Slovakia and the UK), much of which has been introduced or strengthened over the previous five years (see table on p51).
Summary of the Directive
Approved in April 2019, the new EU-wide standards to whistleblowing were nearly unanimously agreed by MEPs – implementing significant new standards to be upheld and processes to be instituted. For reporting certain breaches of EU law, the directive broadly requires employers (except those in the private sector with fewer than 50 employees although exceptions apply) to:
- Make available secure and confidential channels for reporting internally and provide information on how/when to report externally to public bodies/regulators. Internal channels may be operated by a third party.
- Establish procedures for investigating and following up on internal reports within set timescales, including designating an individual or department to diligently perform this role.
- Decide whether to make internal channels available not just to employees but also to others acquiring whistleblowing information in a work-related context, including the self-employed and those working for contractors, suppliers and subcontractors.
- Protect whistleblowers against dismissal, demotion and other forms of retaliation if disclosers had reasonable grounds to believe the information was true at the time of reporting, it fell within the scope of the directive and they complied with its reporting channels.
The directive sets down principles indicating when internal, external or public disclosure is appropriate. For example, public disclosures to the media are protected if, amongst other grounds, the whistleblower has reasonable grounds to believe there is an imminent danger for the public interest or other channels have failed. In the event of retaliation, member states must provide effective sanctions, including interim relief, and whistleblowers are immune from legal proceedings in certain circumstances. No waiver of rights and remedies in the directive are permitted.
Other countries, including non-EU states, have announced new whistleblowing legislation or are in the process of implementing change. For example, Switzerland, Poland, Slovakia, Norway, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates and Australia are all strengthening existing regulation or seeking to introduce new rules on protected disclosures by some sector-specific employees or more broadly. In Asia, Japan’s Consumer Affairs Agency is considering amendments that would see the effectiveness of Japan’s current whistleblower protection laws improve, as well as increase in scope. The changes are expected to go through the legislature in late 2019. Hong Kong has seen increased calls for general whistleblowing legislation following several corporate scandals, and it is only a matter of time before the government responds.
The United States has a long-standing, complex system of whistleblower legislation that includes federal statutes as well as certain state law regimes. Recently, there has been an increase in whistleblowing activity which, is likely to continue. The US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) reported that it awarded more dollars to whistleblowers in 2018 than in all prior years combined. The SEC also has a long-standing policy challenging confidentiality provisions in employee agreements that have the potential to chill whistleblowing activity – a practice that has impacted the drafting of employee-related agreements even for companies not subject to SEC oversight. In a recent development, the US Supreme Court unanimously extended the time for bringing claims in certain cases under the False Claims Act.
The EU Whistleblowing Directive
In April 2019, the EU Parliament agreed to a new directive to protect workplace whistleblowers, revealing breaches of EU law in a wide range of areas including public procurement, financial services, product safety, and consumer and data protection. The law must be approved by EU ministers, after which member states will have two years to make their national rules compliant.
EU states with limited whistleblowing protections currently, such as Germany, Spain and Austria, will be required to introduce wholesale change by 2021. Many others, including Ireland (regarded as having comprehensive rules already in place), will also have to act. For example, widening the scope of protection to volunteers, suppliers and contractors, and introducing a requirement on employers to investigate and provide follow-up reports to disclosers within set time scales.
Practical implications – beyond Europe
Workplace whistleblowers play a significant role in uncovering wrongdoing and alerting employers. Despite this, managers can be wary of whistleblowing channels, fearing malicious reporting.
Diane Gilhooley’s Top Tips
- Does your whistleblowing policy provide accessible and confidential reporting channels that are highly visible and understandable?
- Will your policy adhere to the new EU standards globally, or will it reflect local law?
- Will it be extended to third parties such as those working for suppliers?
- Will financial incentives be offered to whistleblowers, and how is anonymous reporting handled?
- Check whether the policy, and any proposed changes, comply with data protection, works council consultation and other legal requirements.
- Do you have systems for the diligent and timely investigation of reports and for responding to disclosers?
- How are disclosers protected against all forms of retaliation?
- Are managers trained in dealing with reports and supporting disclosers?
- Is whistleblowing actively encouraged – do workers believe that they can and should disclose their concerns, and will be supported to do so?
- How transparent is your whistleblowing policy – where possible, are outcomes shared with workers?
However, these concerns should not cloud the case for instituting a robust whistleblowing system and embedding a culture of speaking up in the organisation’s DNA. Without this, the fear of suffering retaliation will have a chilling effect on whistleblowers, depriving employers of the opportunity to investigate and address issues away from the glare of publicity and the attention of both government bodies and the courts. A 2017 EU survey found that 85% of respondents would rarely report wrongdoing, fearing negative repercussions.
The changing legal landscape, spearheaded by the EU Directive, requires employers to review existing whistleblowing procedures for compliance. At the same time, employers should take this opportunity to assess their own whistleblowing culture. Like with GDPR, which forced businesses to take an honest look at their data handling and protection policies, this latest EU legislation will prompt many to review key elements of their whistleblowing systems – including leadership, commitment and accountability.
After all, good governance should encourage workers to speak up internally – for the sake of the company’s health, longevity and financial wellbeing.